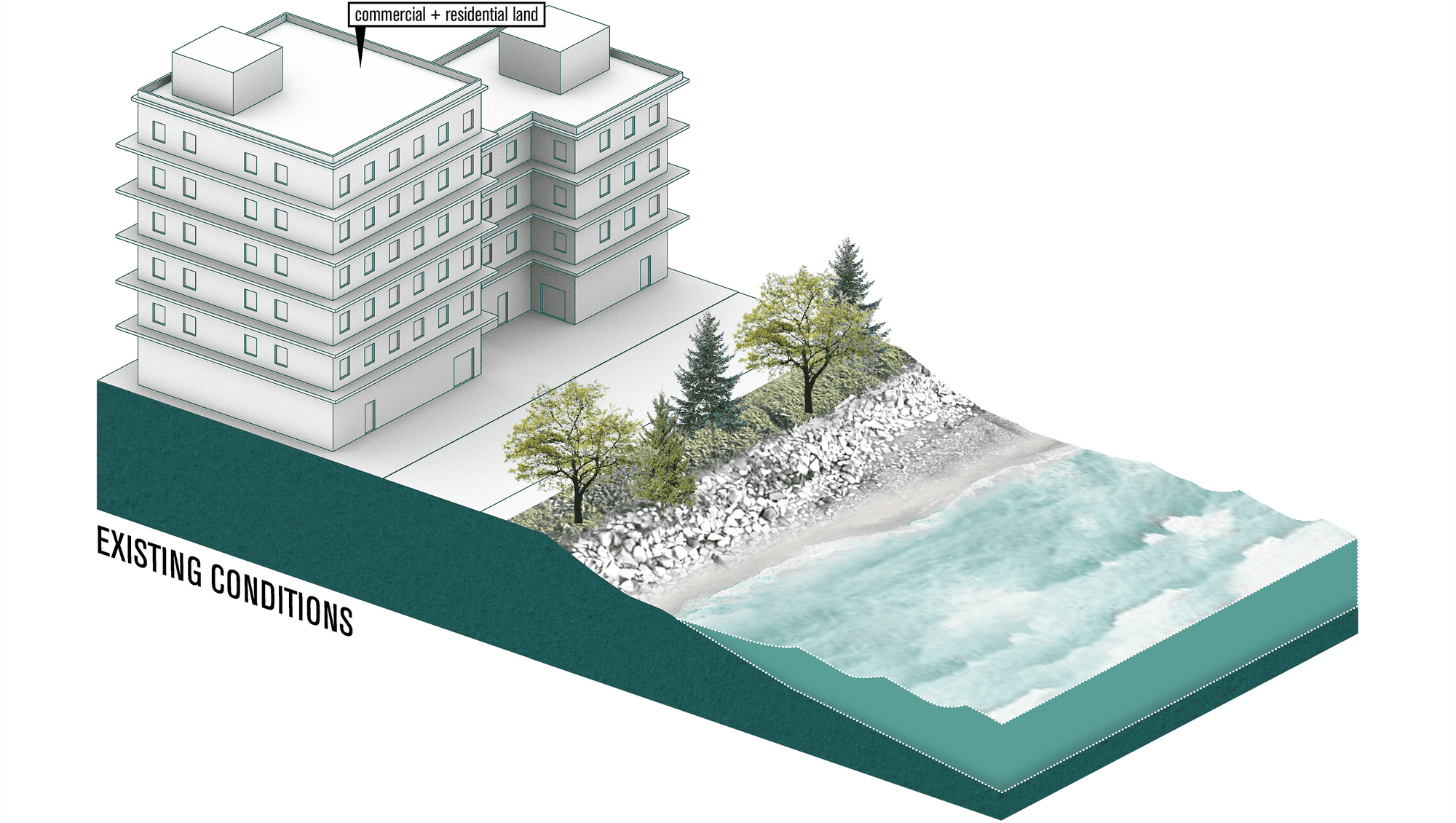
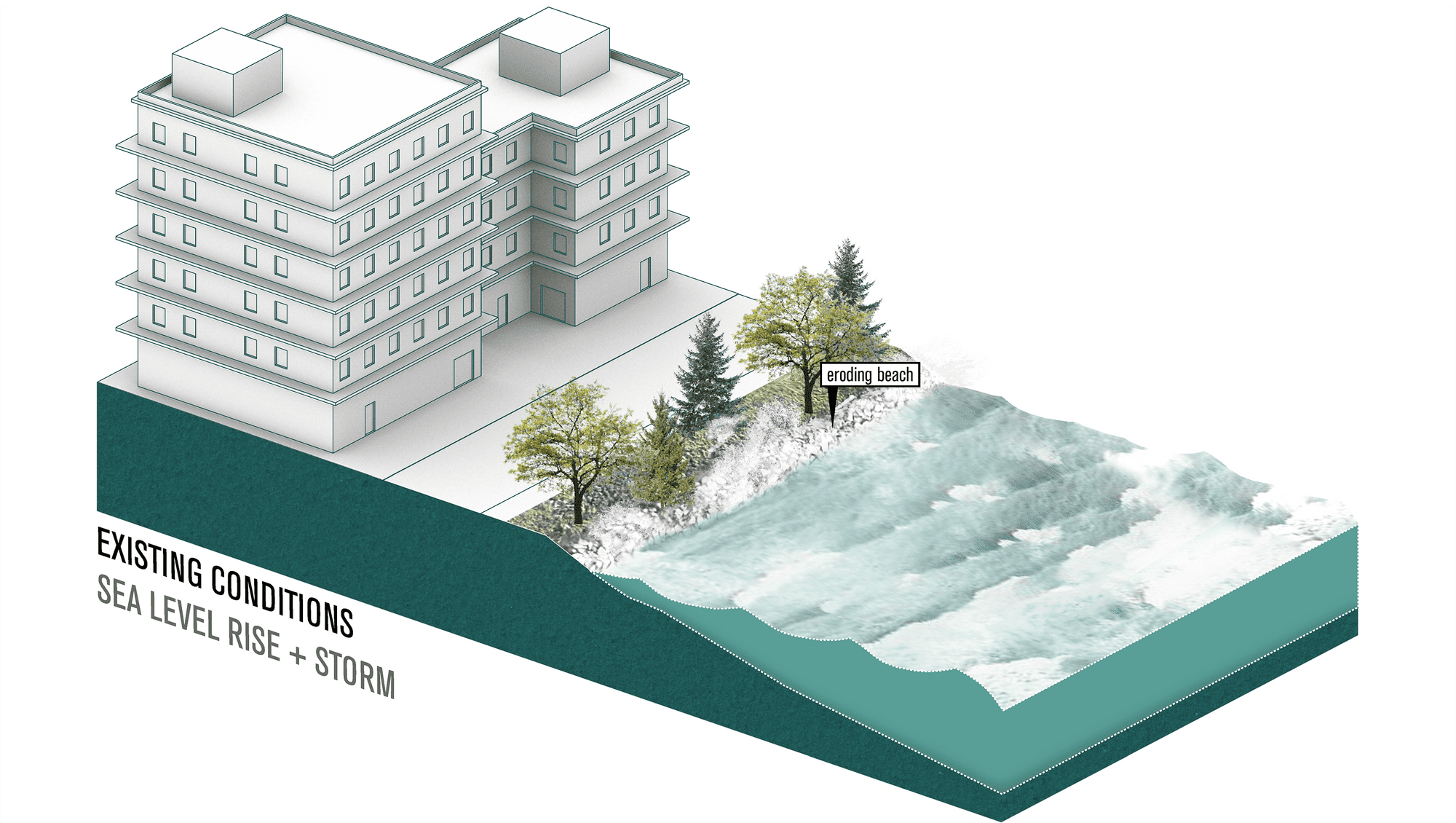
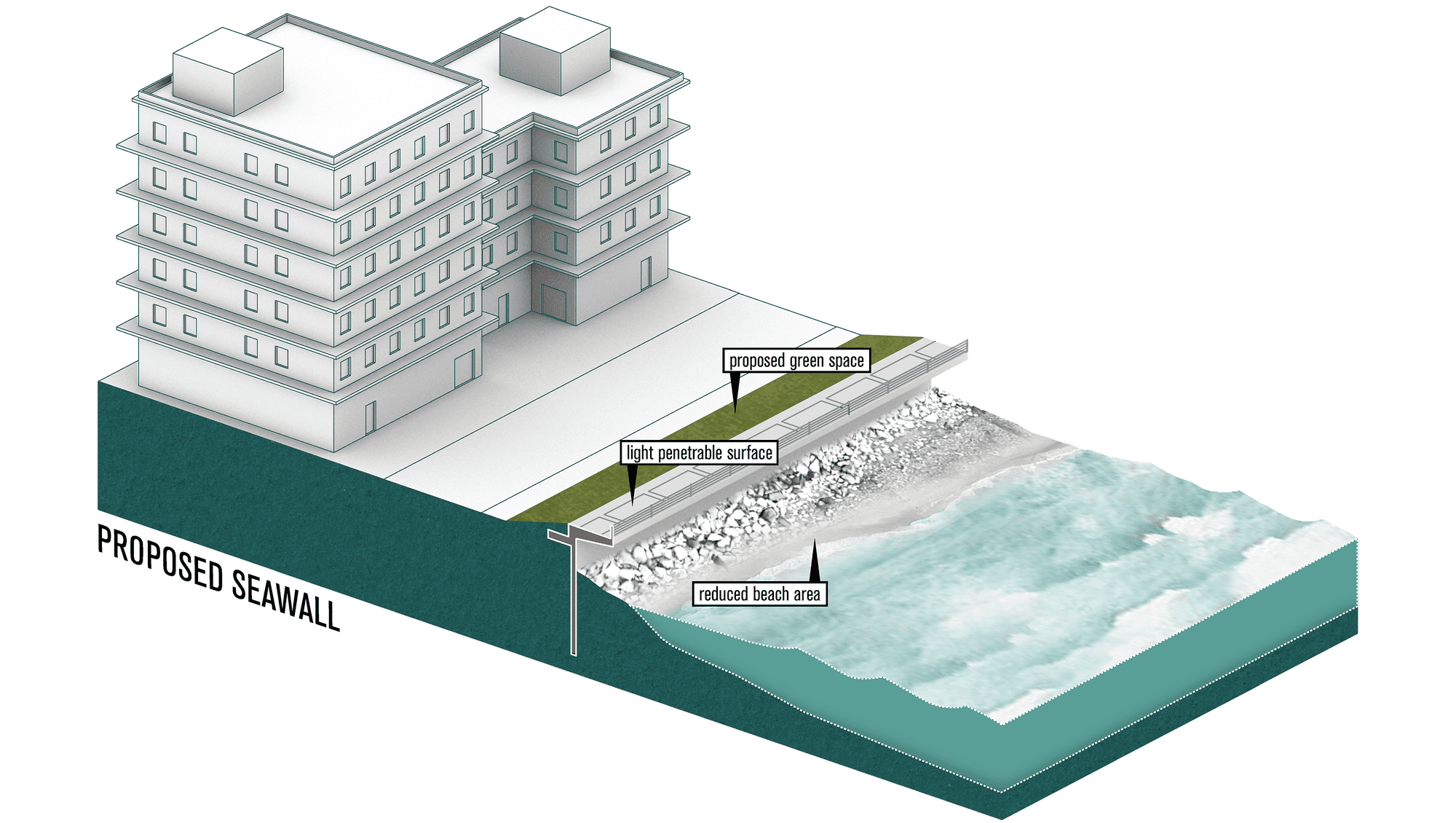
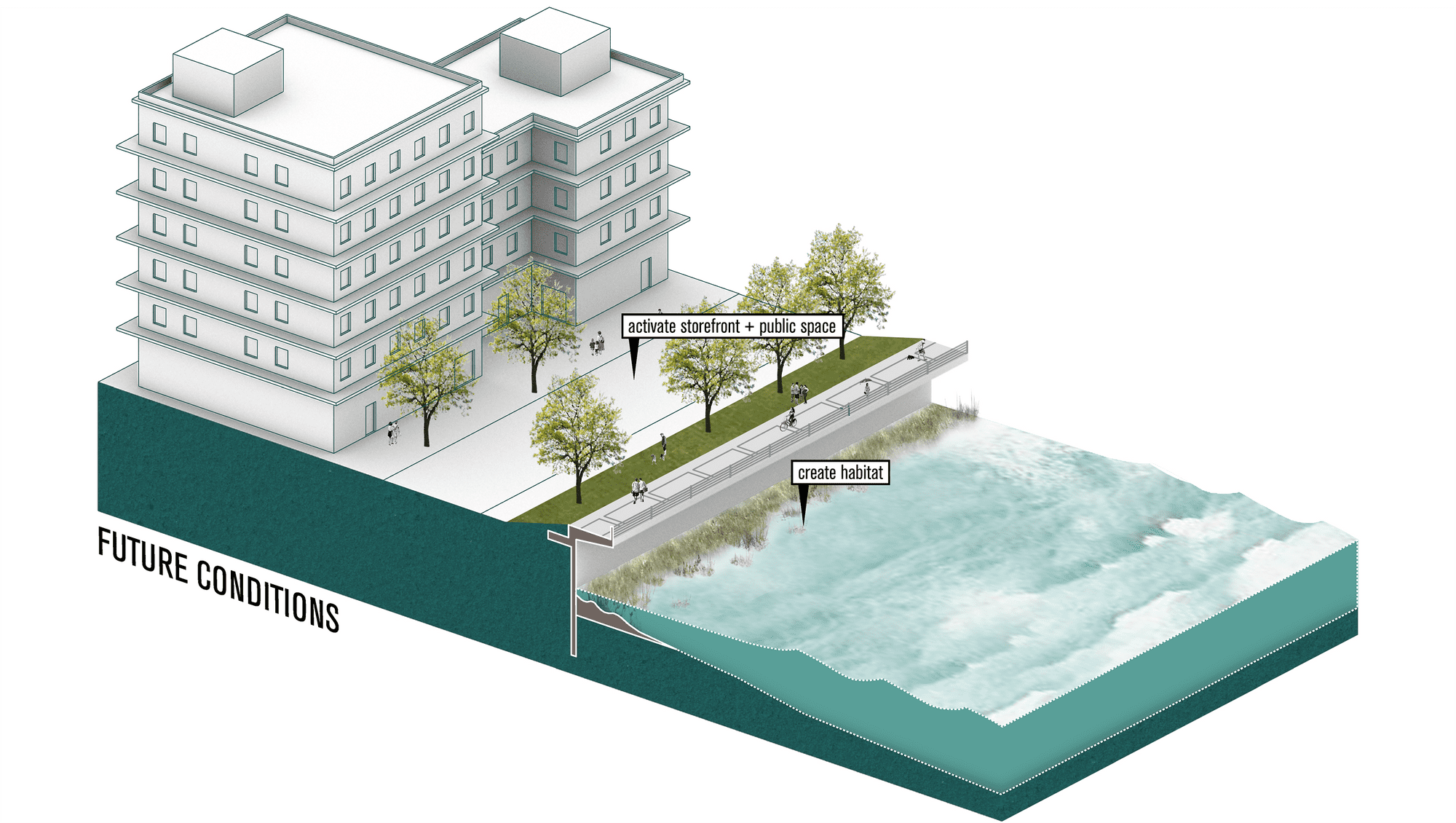
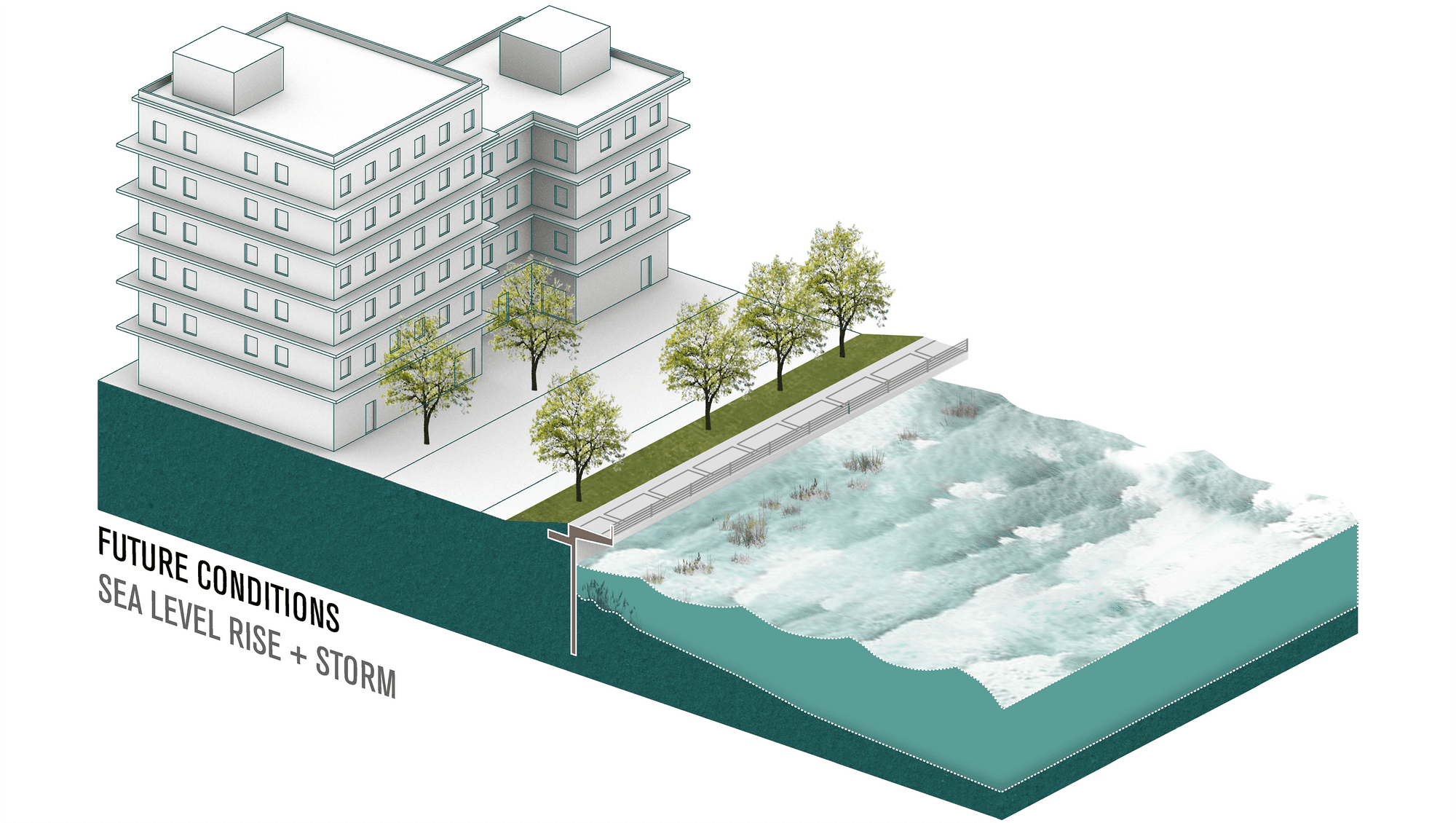
Adaptation Strategy: Seawall
Seawalls are hard engineered structures built parallel to the shoreline. They have a lower requirement for space than dikes and therefore can be constructed in smaller spaces. 1 Seawalls can be constructed using various materials including reinforced concrete, boulders, steel, or gabions.2 Seawalls serve as the first line of defense during, a storm surges, by protecting coastal infrastructures from wave impact.3
How it works
Types of seawall
- Steel sheet pile walls comprise interlocking steel sheets anchored deep beneath the surface of the ground. They are ideally suited for areas with less intense wave and storm surge activity.
- Gravity walls depend on the weight of its constituent materials to stabilize the wall in the ground. Therefore, they require stable soil conditions and reinforcement around the base to buffer the effects of shearing.
- Curved walls are designed with a sweeping curve that helps to dissipate wave impact deflecting it upwards from the base of the wall. Curved walls are designed to reduce the effects of scouring, i.e., removal of sediments from the base of the wall.
- Brick or block walls or gabions (wire baskets filled with rocks) comprise of walls constructed from concrete blocks and rocks installed on a man-made slope. The slope shape helps to dissipate the force of the wave 6
Benefits
- Provides protection against coastal flooding and erosion.
- Unlike other sea defense systems, sea walls can be constructed in smaller spaces.
- Possess higher amenity value when compared to other defense structures such as dykes
- Has long shelf life in excess of 100 years compared to soft sea defense approaches, e.g., beach nourishment.
Challenges
- Wave impact exerts a significant load on sea walls which tends to increases water dept at the front of the wall
- Reflects wave energy seawards creating turbulence and nearshore erosion
- Causes sediment starvation where erosion in front of the seawall occurs at a faster rate than sediment is deposited through the erosion of the hinterland. This can lower the profile of the beach.
- Prevents the natural inland migration of coastal systems thereby causing coastal squeeze. This leads to a reduction in intertidal habitats such as sandy beaches and saltmarshes 6
Example projects
The Seattle Seawall
The Seattle Seawall was originally built in 1920 and 1936, however, in 2001 and 2004, concerns about the structural integrity of the wall arose. The City of Seattle put forth the Central Seawall Project to replace the 3,700 ft of the seawall with a new seismic-resistant seawall. In addition to the state-of-the-art seawall, the project was also intended to create an unprecedented salmon migration corridor, an enhanced shoreline ecology, and an aesthetically pleasing promenade.3 The seawall features light penetrable surfaces that allow sunlight under the cantilevered where textured concrete panels and habitat benches provide habitat for juvenile salmon.
Stanley Park Seawall
Vancouver BC, Canada
The Stanley Park Seawall is one of the most popular landmarks in Vancouver. It is part of the waterfront path that connects Stanley Park, False Creek, and the Spanish Banks. The construction of the Seawall began in 1917 and was completed in 1980.4 After 1980, the Seawall continued to expand outside of Stanley Park. The Seawall near Second Beach and Sunset Beach was upgraded in 2010 and 2011 to address the erosion concerns that were caused by stroms.5
Citations
-
1.
↑
Climate Technology Centre and Network. Sea Walls. https://www.ctc-n.org/technologies/sea-walls
-
2.
↑
The Arlington Group Planning Architecture Inc., et al. Sea Level Rise Adaptation Primer. pp. 68. https://www2.gov.bc.ca/assets/gov/environment/climate-change/adaptation/resources/slr-primer.pdf
-
3.
↑
“Central Seawall Project: 2017 ASLA Professional Awards.” Central Seawall Project | 2017 ASLA Professional Awards, https://www.asla.org/2017awards/320768.html.
-
4.
↑
Vancouver, City of. “The Seawall in Vancouver.” City of Vancouver, https://vancouver.ca/parks-recreation-culture/seawall.aspx.
-
5.
↑
Ibid.
-
6.
↑
Salgardo, J. (2017) Types of Seawalls. Sciencing. https://sciencing.com/types-seawalls-8394254.html
-
i1.
↑
Magnusson Klemencic Associates. A Vehicular-Rated Railing Allows Pedestrians to Look over the Bay While Standing on Top of the Cantilevered LPS. https://www.asla.org/2017awards/images/320768/320768_8.jpghttps://www.asla.org/2017awards/images/320768/320768_8.jpg.
-
i2.
↑
Seawall Along Stanley Park. https://quietly-image-uploads.s3.amazonaws.com/item_57095_640px_69b7bbcd8b0143eaa8b3a67ab9d4d856.jpeg.
-
i3.
↑
Figure 1. Melville, D and Chen, Y. (2014). The Great Seawall of China Threatens a Quarter of the World's Shore Birds http://www.takepart.com/article/2014/11/20/great-seawall-china-threatens-quarter-worlds-water-birds
-
i4.
↑
Figure 2 Israel, M. H. (2014). Seawalls Units Herzliya Marina. https://econcretetech.com/seawall-units-herzliya-marina/
-
i5.
↑
Figure 3. O’Neill, E. (2018). Seattle's New Seawall Is Built To Help Salmon https://www.opb.org/news/article/seattle-seawall-new-salmon-juvenile/